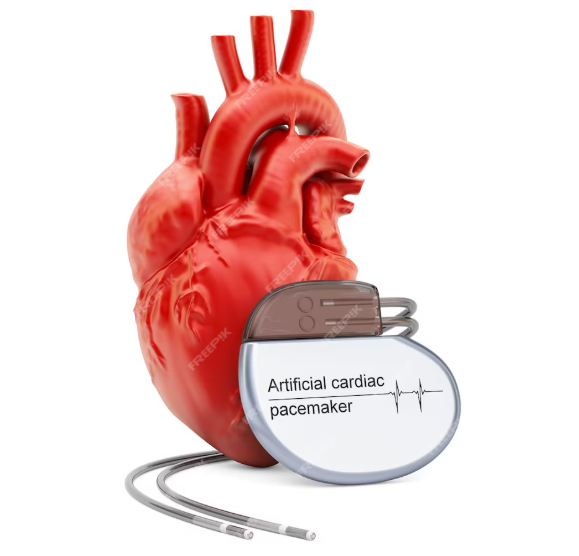
A pacemaker is a small, implantable medical device that helps regulate abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). It’s placed under the skin, usually near the collarbone, during a minor surgical procedure. The device uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate if it detects a rhythm that’s too slow, irregular, or paused.
Key features:
– Components: A battery-powered generator and thin wires (leads) that connect to the heart.
– Conditions treated*: Often used for bradycardia (slow heartbeat), fainting spells, or heart block.
– Adjustability: Monitors heart activity 24/7 and adjusts therapy automatically.
Modern pacemakers are long-lasting (5–15 years), lightweight, and often integrate with remote monitoring systems for check-ups. They allow most people to resume daily activities safely. Always follow your doctor’s guidance on precautions (e.g., avoiding strong magnetic fields).